
 |
 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Clinical studies It's not fiction, it's medical reality
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
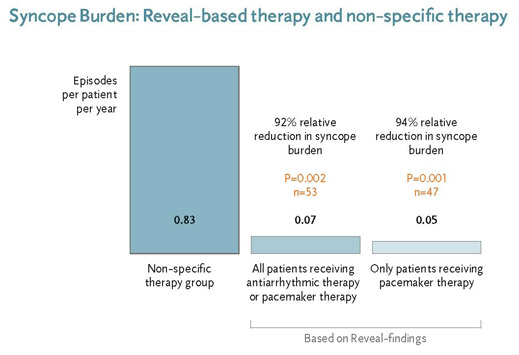
The efficacy of a diagnostic strategy using a Reveal to guide therapy selection was assessed in patients with suspected Neurally Mediated Syncope (more than three severe episodes in two years). For 103 patients Reveal documented the first syncope recurrence. The subsequent treatment was then evaluated.
Reveal documented bradycardia or asystole in 47 patients, who received pacemaker therapy. In 6 others Reveal documented tachyarrhythmia. These patients received catheter ablation, ICD therapy or antiarrhythmic therapy.
For the patient group receiving specific therapy, a 92% relative reduction in syncope burden was realized, compared to the group receiving non-specific therapy. The subset of patients who received a pacemaker, showed a 94% relative reduction in syncope burden.
Early application of Reveal guides effective therapy in syncope patients.
A Reveal-based therapy led to a major reduction in syncope recurrence. Early use of Reveal is recommended.
International Study on Syncope of Uncertain Etiology 2 (ISSUE 2)
M. Brignole et al; European Heart Journal, 2006